국제경영론 International Business
Chapter. National Differences in Political Economy &Economic Development
- what is political economy?
- refers to its political,economic, and legal systems
- These systems are interdependent, and interact and influence each other
- A country’s political economic system has major implications for the practice of international business (한 나라의 정치 경제 체제는 국제적인 사업의 실행에 주요한 영향을 미침)
states in transition
- trend in political economy since late 1980s
- A wave of democratic revolutions swept the world and many previous totalitarian regimes collapsed
- A move away from centrally planned and mixed economies towards free markets
- A shift back toward greater authoritarianism in some nations and signs of a retreat from the free market model
- spread of democracy
- Many totalitarian regimes failed to deliver economic progress to majority of population
- New information and communication technologies have broken down ability of state to control access to uncensored information
- Economic advances of last quarter century led to increasingly prosperous middle and working classes who pushed for democratic reforms
- political freedom in the world
- spread of market based system
- 1980년대 후반에 market economy의 부상, 이유는 command economy의 inefficiency 가 밝혀짐
- Since the late 1980s, a transformation from centrally planned command economies to market-based economies
- Command and mixed economies failed to deliver the sustained economic performance achieved by countries that had adopted market-based systems
- Many countries shifted to a market-based system
- the nature of economic transformation
- The shift toward a market-based economic system typically involves at least three distinct activities:
- Deregulation
- Involves removing legal restrictions on the free play of markets
- The establishment of private enterprises
- Removing price controls
- free trade, business friendly, nonintervention, open opportunitiess, removing barrier, limited oversight
- Privatization
- Transfers the ownership of state property into the hands of private investors
- Because private investors are motivated by potential profits to increase productivity, privatization should increase economic efficiency
- ex. british telecom (bt) &indian oil and gas sector,
- ex. aerolineas argentinas; railtrack in the UK
- Legal system
- A well-functioning market economy requires laws protecting private property rights and providing mechanisms for contract enforcement
- Without a legal system that protects property rights, and without the machinery to enforce that system, there is little incentive to engage in economic activity
- legal system : give assuarance of assets , singapore은 잘 작동하는 legal system으로 유명함
- Deregulation
- The shift toward a market-based economic system typically involves at least three distinct activities:
- implication for managers
- the political, economic, and legal environment of a country clearly influences the attractiveness of that country as a market and/or investment site
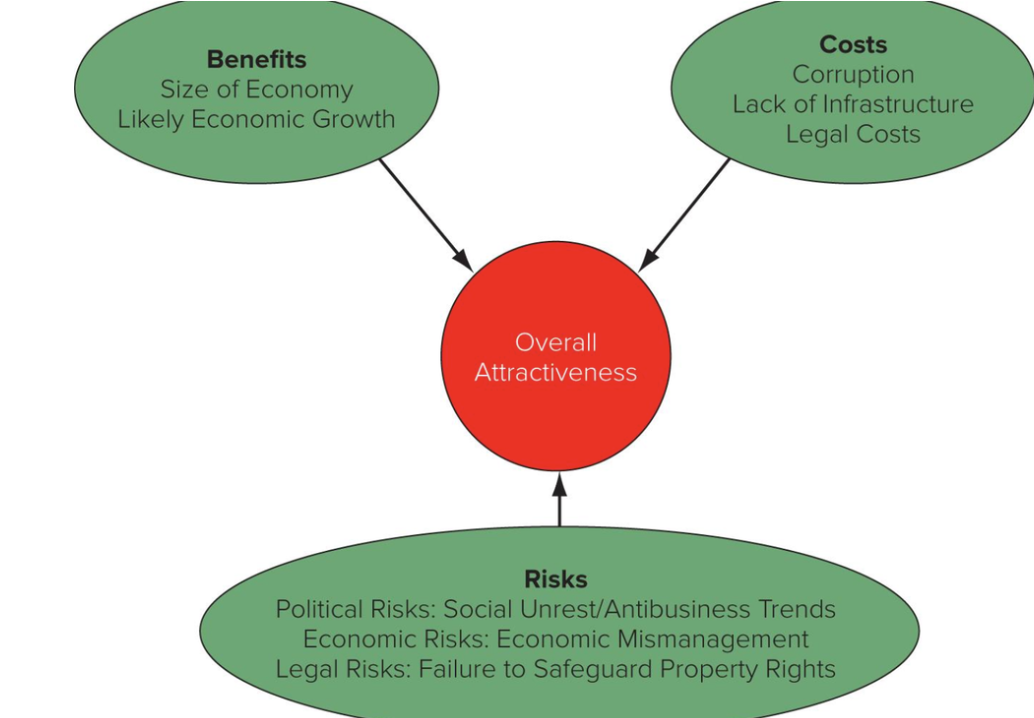
- overall attractiveness
- The overall attractiveness of a country as a potential market and/or investment site for an international business depends on balancing the benefits, costs, and risks associated wit h doing business in that country
- Generally, the costs and risks are lower in economically developed and politically stable markets
- However, the potential for growth may be higher in less developed nations
country attractiveness
pastel analysis

728x90
반응형