국제경영론 International Business
Chapter. Global Production and Supply Chain Management
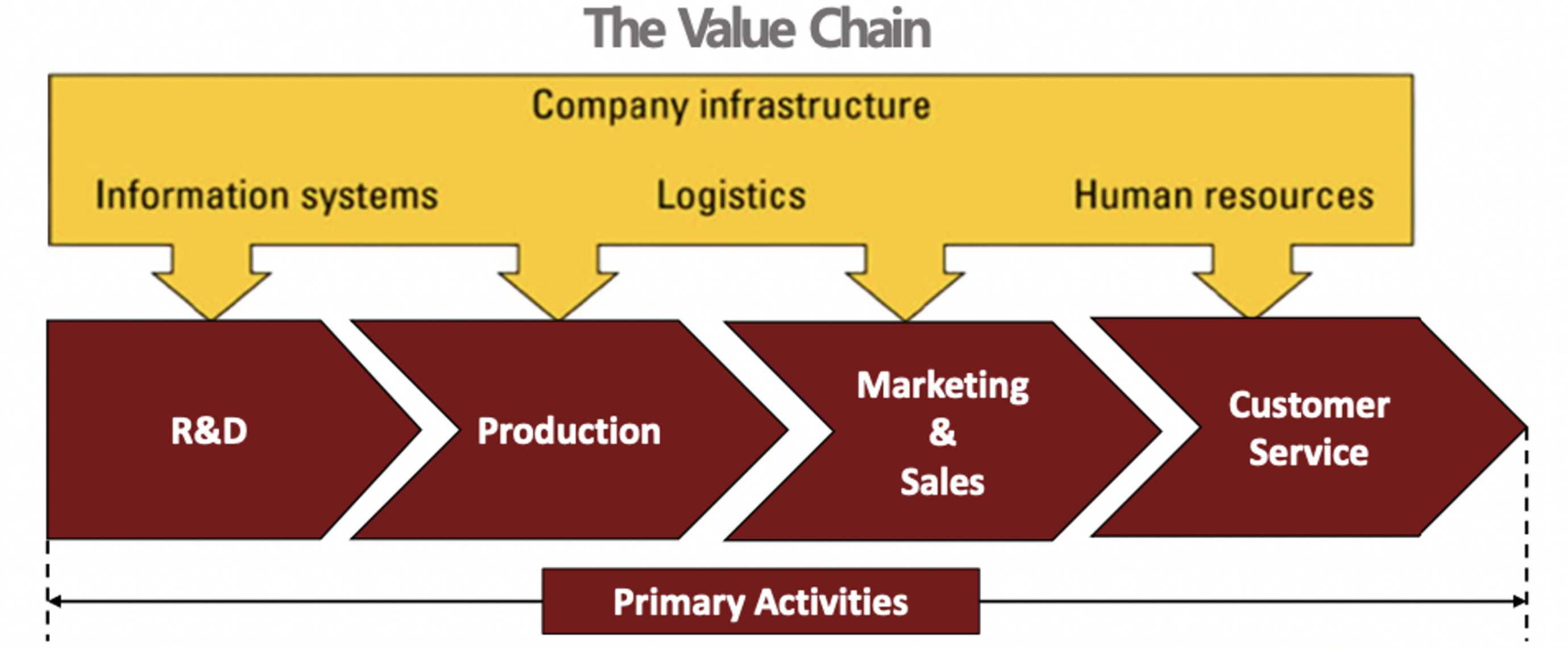
- firms as a value chain
- firms are essentially value chains composed of series of distinct value creation activities, including materials management, human resource, information system, and firm infrastructure
- value creation activities categorized
- primary activity : production, marketing & delivering the product to buyers, and providing support & after-sale service to the buyers
- support activity : help firm to add value
- provide inputs that allow primary activities of production and marketing to occur (information system, communication within the firm, logistic, human resources,, )
- interrelated issues in global economy
- where to locate production activities
- what the long term strategic role of foreign production sites should be
- whether to own or outsource foreign production activities
- how to manage a globally dispersed supply chain and what the role of technology should be in the management of global logistics
- whether to manage global logistics or outsource
Global production : manufacturing activities
생산 시설과 회사를 어디에 위치시킬지
- must consider : (1) country factors, (2) technological factors, (3) production factors
- locating production facility 2가지 전략 존재
- concentrating
- Companies choose one best location for manufacturing.
- They make and ship their products to the world from this place.
- This strategy can save money through large-scale production.
- It also allows companies to control operations tightly.
- The best location is often where costs are low and resources are nearby.
- Factors like skills, transportation, and material access influence this choice
- Decentralizing
- Companies set up many factories in different regions or countries.
- These factories are close to the big markets they serve.
- Being near customers helps companies react quickly to their needs.
- This strategy can cut down on shipping costs and delays.
- It also helps reduce the risk of problems like political trouble.
- Having factories spread out lets companies adjust products for each area's taste or rules.
- concentrating
- country factors : 경제, 정치, 문화, 상대비용적인 조건을 고려 → select most conducive to the performance of activity (stability, cost of input such as labor)
- location externality : Presence of global concentrations of activities (특히, 숙련된 노동자의 능력이나 supporting industries can be key reasons for choosing location
- Regulations affecting FDI and trade barriers : ex. expectations about future exchange rate changes
- transportation cost
- technological factors
- fixed cost : setting up a manufacturing plant are very high → serve the world market from a single location or from a very few locations
- flexibility of technology : Flexible manufacturing technology → wide variety of end products
- Mass customization implies → firm may be able to customize its product range to suit the needs of different customer groups without bearing a cost penalty→ So, firms can act like a local firm without bearing the costs of establishing local manufacturing facilities
- → improve competitive position of firms by allowing the firm to customize products to meet the demands of small customer groups in different markets
- Q. when does it make sense to concentrate production at a few choice locations?
- Concentrated production : fixed costs high, minimum efficient scale of production high,flexible manufacturing technologies are available
- Concentrated not!! : both fixed costs and minimum efficient scale of production are low, flexible manufacturing technologies are not available
- production factors : two product factors impact location decisions
- product’s value-to-weight ratio
- high: a single location and export it ↔ low (like a bottle of water) multiple locations across the world (close to the local market)
- Whether the product serves universal needs→ The need for local responsiveness is reduced for products, which increases the attractiveness of concentrated manufacturing
- (모두가 프로덕트를 같은 방식으로 이용한다면 → u dont need to change it market by market), (국가마다 ,사람마다 다른 방식 이용 → customization 필요)
- product’s value-to-weight ratio
- strategic roles for production facilities
- MNEs used to established and managed foreign plants to benefit only from:
- (1) tariff and trade concessions (2)cheap labor (3) capital subsidies (4) reduced logistics costs.
- Today, MNEs use foreign factories not only to gain access to the usual incentives but also to:(3) create centers of expertise for the entire company (4) global learning!
- (1) get closer to their customers and suppliers (2) attract skilled and talented employees
- Foreign factories can have a number of roles or designations:
- Offshore factory: a factory that is developed and set up mainly for producing component parts or finished goods at a lower cost than producing them at home or in any other market
- Source factory: factory whose primary purpose is also to drive down costs in the global supply chain (expertise o)
- Server factory: factory that is linked into the global supply chain for a global firm to supply specific country or regional markets around the world
- Contributor factory: A factory that serves a specific country or world region
- Outpost factory: A factory that can be viewed as an intelligence–gathering unit
- Lead factory: A factory that is intended to create new processes, products, and technologies that can be used throughout the global firm in all parts of the world
- Q. does strategic rationale for establishing a foreign production facility change?
- The strategic role of foreign factories and the strategic advantage of a particular location can change overtime
- factory initially established to make a standard product to serve a local market, or to take advantage of low-cost inputs, can evolve into a facility with advanced design capabilities
- As governmental regulations change and/or countries upgrade their factors of production, the strategic advantage of a particular location can change
- As the strategic role of a factory is upgraded and a firm develops centers of excellence in different locations worldwide, it supports the development of a transnational strategy
- A focus of a transnational strategy is global learning:the idea that valuable knowledge does not reside just in a firm’s domestic operations, it may also be found in its foreign subsidiaries
- Managers should promote the idea that factories are potential centers of excellence with strategic importance to the firm
- Answer: yes (role of foreign factory change o )
728x90
반응형
'국제경영론IB' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [국제경영론] Global Marketing and R&D (0) | 2024.01.02 |
|---|---|
| [국제경영론] Global Production and Supply Chain Management (2) (0) | 2024.01.01 |
| [국제경영론] Entering foreign markets (2) (1) | 2023.12.31 |
| [국제경영론] Entering foreign markets (1) | 2023.12.30 |
| [국제경영론] The strategy of international business (2) | 2023.12.29 |


