국제경영론 International Business
Chapter. Global Marketing and R&D (2)
global R&D
- traditional centralized approach to R&D
- Traditional centralized approach to R&D will no longer suffice (less effective bcs single location of R&D project is not effective bcs of rapid pace of tech change) → 변화 방향 : speedy in product development + align with global strategy
- as more and more sources of potentially relevant knowledge emerge across globe
- R&D를 다른 국가에 설치하면 → 더 넓은 지식과 학문, 연구 등에 접근할 수 있음
- companies competing around the world must move new products from development to market at an ever more rapid pace
- rapid commercialization: accelerate develop of new product → company to innovate and respond more quickly to market demand → global R&D network help company to act more quickly
- as more and more sources of potentially relevant knowledge emerge across globe
- Traditional centralized approach to R&D will no longer suffice (less effective bcs single location of R&D project is not effective bcs of rapid pace of tech change) → 변화 방향 : speedy in product development + align with global strategy
- building effective R&D capabilities abroad
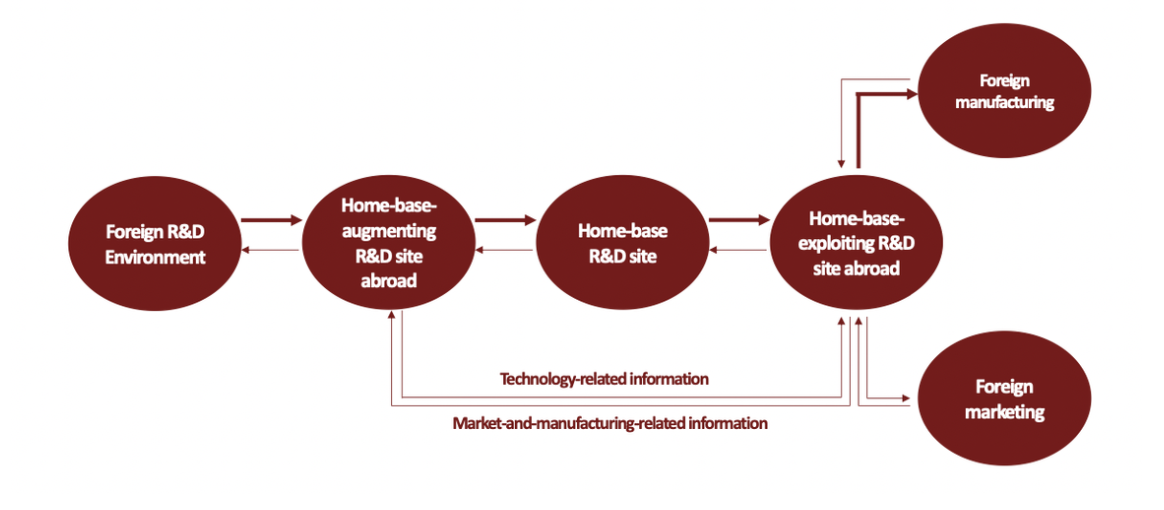
- Home-base-augmenting R&D siteInformation flows from the foreign laboratory to the central lab at home
- Phase 1: Choosing a Location for the Site
- Selecting a location for its scientific excellence
- Absorbing new knowledge can happen:
- through participation in formal (ex. Industrial liaison programs with Stanford U.) or informal meeting circles in a knowledge cluster(ex. Silicon Valley),
- through hiring employees from competitors,
- through sourcing laboratory equipment and research services from the same suppliers that competitors use
- Phase 2: Start-up Period
- (랩 리더 정하기, 첫번째 리더는 유명한 사람이 좋음) for first lab leader, choose a renowned local scientist with international experience - one who understands dynamics of R&D at the new location
- by leveraging the renowned leader, bring in additional outstanding local scientists
- to integrate new site into the company as a whole, senior management at home must integrate site’s research agenda into the company’s overall strategic goals
- Phase 3: Maximizing Lab Impact
- Ensure the lab’s active participation in the local scientific community by nurturing ties between the new site and the local scientific community
- Exchange researchers with local university labs, home-base-exploiting labs, and the central R&D (local entity, ,, → excellerate R&D activity)
- Connect&develop
- Open innovation
- Phase 1: Choosing a Location for the Site
- Tap knowledge from competitors and universities around the globe
- Home-base-exploiting R&D siteInformation flows from the central lab at home to the foreign laboratory
- Phase 1: Choosing a Location for the Site
- Should be located close to large markets and manufacturing facilities in order to commercialize new products rapidly in foreign markets. (in terms of logistic, responsiveness to market change, integration with production process 측면에서 효율적임)
- Involve middle managers from other functional areas in start-up decisions (R&D activity closely tide to supply chain, marketing, local business,,, )
- Phase 2: Start-up Period
- For 1st lab leader, choose an experienced product development engineer with a strong companywide reputation, international experience, and knowledge of marketing and manufacturing (experience, deep understanding) (marketing and production is key word of this R&D)
- Primary responsibility: Forge close ties between the new lab’s engineers and the foreign community’s manufacturing and marketing facilities. (fostering trust)
- Phase 3: Maximizing Lab Impact
- Emphasize smooth relations with the central R&D.
- Encourage employees to seek interaction with other corporate units beyond the manufacturing and marketing units that originally sponsored the lab
- Tight cross-functional integration leads to:
- Product development projects driven by customer needs (R&D and marketing);
- New products designed for ease of manufacture (R&D and production);
- Development costs kept in check (R&D and production);
- Time to market minimized (R&D and production).
- Phase 1: Choosing a Location for the Site
- Support manufacturing facilities in foreign countries or to adapt standard products to the demand there.
- Home-base-augmenting R&D siteInformation flows from the foreign laboratory to the central lab at home
- two types of r&d sites (remember the direction)
- how information flow between home-base and foreign R&D sites
728x90
반응형
'국제경영론IB' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [국제경영론] Globalization_세계화, changing demographics of global economy, multinational enerprise (0) | 2024.01.07 |
|---|---|
| [국제경영론] Globalization_세계화, global economy, drivers of globalization (0) | 2024.01.06 |
| [국제경영론] Global Marketing and R&D (0) | 2024.01.02 |
| [국제경영론] Global Production and Supply Chain Management (2) (0) | 2024.01.01 |
| [국제경영론] Global Production and Supply Chain Management (1) | 2024.01.01 |
